Cost-effective clinical trials
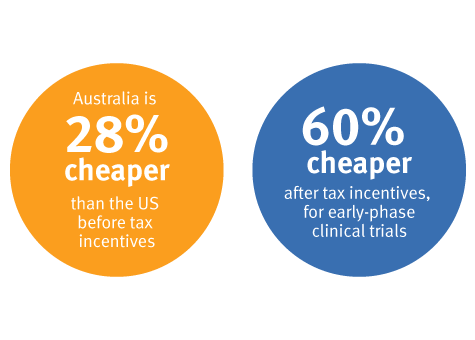
It is up to 60% cheaper to conduct clinical trials in Australia compared to the USA1.
What are the attractive tax incentives?
Every year, more than 1000 new clinical trials commence in Australia by pharmaceutical, biotechnology and medical device companies.
Commercial sponsors take advantage of competitive clinical trial costs in Queensland. Learn more about research and development tax incentives.

Research and Development Tax Incentive program
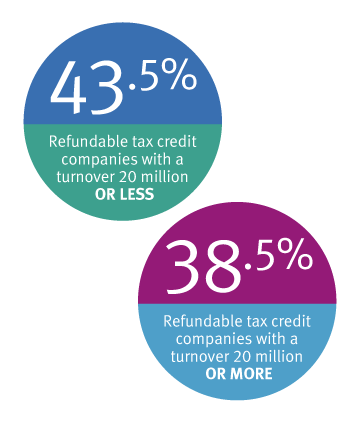
Eligible companies can take advantage of the Research and Development (R&D) Tax Incentive program with a cash refund of up to 43.5% on qualifying* R&D expenditure.
The Tax Incentive program provides targeted R&D tax offsets to encourage more companies to engage in research in Australia. The R&D tax incentive has two core components.
- Companies with an annual turnover of $20 million or less
- Companies with an annual turnover of $20 million or more
Unlike similar programs in other countries, there is no requirement for companies in Australia to demonstrate year-on-year growth in their R&D expenditure to claim a tax benefit.
It’s also not a requirement for the intellectual property from eligible R&D projects to be held in Australia. Learn more about the program.
Eligibility
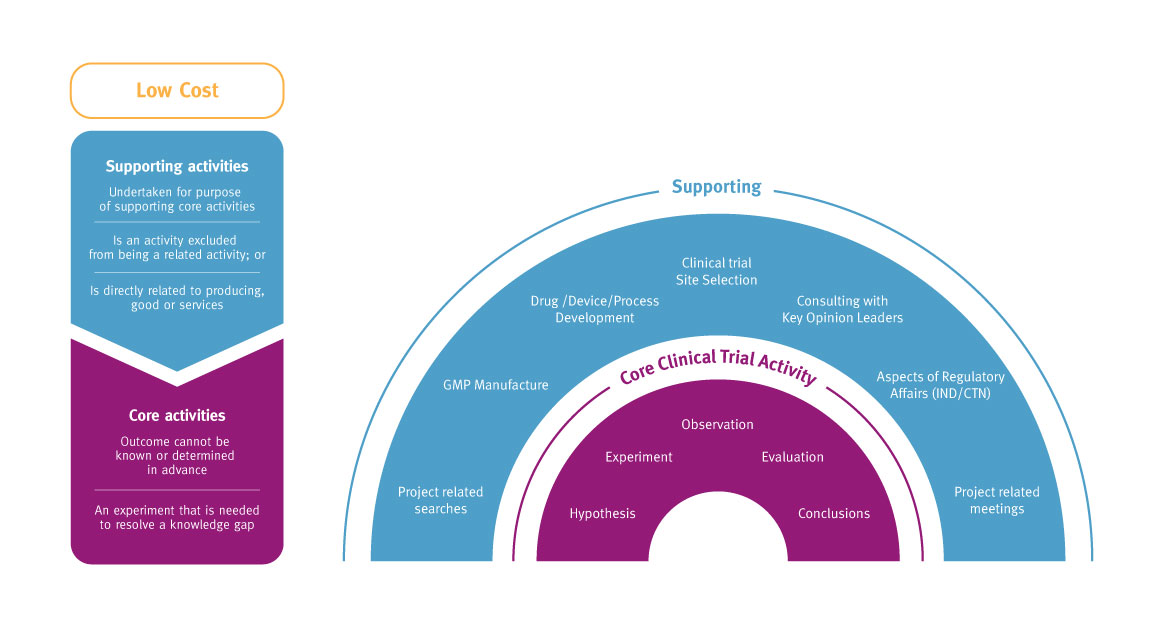
Generally, activities conducted in Australia during early stage development or clinical trials (phases 0/I, II and III) are likely to meet the eligibility criteria.
There is no Investigational New Drug (IND) requirement in Australia allowing rapid entry into clinical trials under the Clinical Trials Notification scheme (CTN). The CTN is administered by the Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA).
To find out more, visit the TGA or business.gov.au.
1 https://www.outsourcing-pharma.com/Article/2016/10/26/Report-Australia-…
*Clinical research activities qualify as core R&D and are experimental activities: the outcomes cannot be known or determined in advance on the basis of current knowledge, information or experience. Outcomes can only be determined by applying a systematic progression of work that is based on principles of established science, proceeds from hypothesis to experiment, observation and evaluation, and leads to logical conclusions. The core activity is conducted for the purpose of generating new knowledge (including new knowledge in the form of new or improved materials, products, devices, processes or services).
